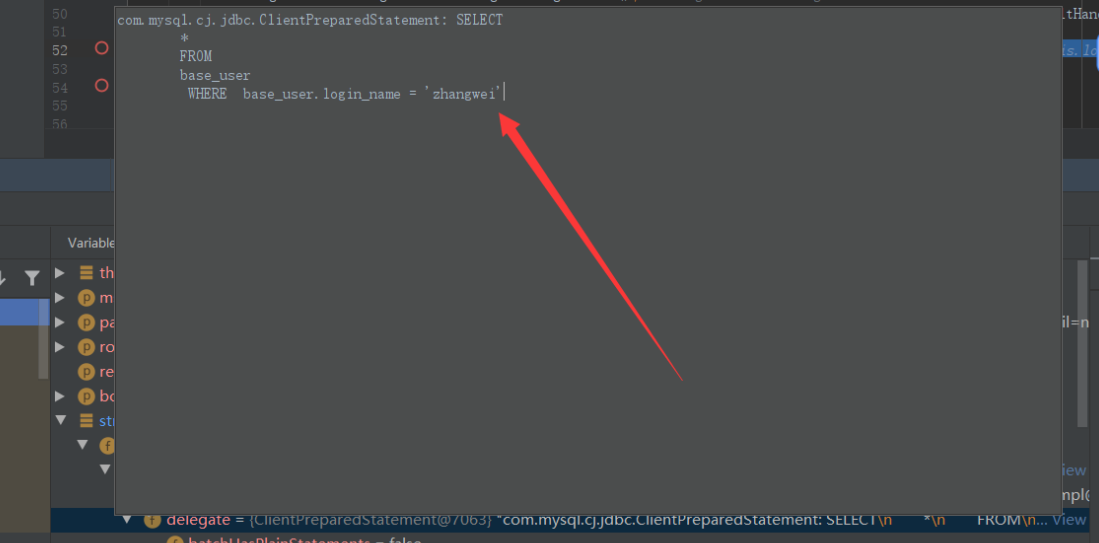
Mybatis组件ParameterHandler源码分析
1. ParameterHandler
在之前的分析文档中,我们了解到在创建StatementHandler时,会生成参数处理器及结果集处理器。每个StatementHandler都会包含一个ParameterHandler及ResultSetHandler。ParameterHandler参数处理器主要是为PreparedStatement的sql语句参数动态赋值。
this.parameterHandler = this.configuration.newParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
this.resultSetHandler = this.configuration.newResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, rowBounds, this.parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql);
2. 源码分析
2.1 SqlSource
SqlSource是一个接口,只有一个方法,根据参数对象获取BoundSql,它的主要功能就是从XML文件,然后根据输入参数创建SQL将其传递到数据库执行。
BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject);
它的实现类如下所示:
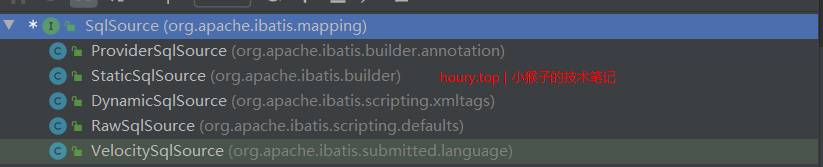
DynamicSqlSource :封装动态SQL标签解析之后的SQL语句和带有${}的SQL语句,${}和动态标签中的表达式是都OGNL表达式,都是使用OGNL表达式从入参对象中获取。
RawSqlSource : 主要封装带有#{}的SQL语句或者可直接执行的SQL语句,则使用该SqlSource来封装SQL信息。
StaticSqlSource : 处理静态sql,无论是静态sql,还是动态sql,最终的处理结果,都是静态sql。
ProviderSqlSource :处理注解Annotation形式的sql。
2.2 ParameterHandler接口
ParameterHandler是一个接口,定义个两个方法,也只有一个实现类。比较简单。
ParameterHandler接口源码:
/**
* A parameter handler sets the parameters of the {@code PreparedStatement}
* 参数处理程序设置 {@code PreparedStatement} 的参数
*
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public interface ParameterHandler {
//得到参数
Object getParameterObject();
//设置参数
void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException;
}
2.3 DefaultParameterHandler
DefaultParameterHandler,默认的参数处理器,是 ParameterHandler接口的实现类,主要是提供了处理参数的实际逻辑。
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
* @author Eduardo Macarron
* 默认参数处理器
*/
public class DefaultParameterHandler implements ParameterHandler {
private final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry;
private final MappedStatement mappedStatement;
private final Object parameterObject;
private final BoundSql boundSql;
private final Configuration configuration;
public DefaultParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
this.mappedStatement = mappedStatement;
this.configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration();
this.typeHandlerRegistry = mappedStatement.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry();
this.parameterObject = parameterObject;
this.boundSql = boundSql;
}
@Override
public Object getParameterObject() {
return parameterObject;
}
//设置参数
@Override
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
//设置参数
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
//循环设参数
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
//如果不是OUT,才设进去
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
//若有额外的参数, 设为额外的参数
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
//若参数为null,直接设null
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
//若参数有相应的TypeHandler,直接设object
value = parameterObject;
} else {
//除此以外,MetaObject.getValue反射取得值设进去
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
//不同类型的set方法不同,所以委派给子类的setParameter方法
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
}
3. 流程分析
3.1 SqlSource
我们知道,项目在启动时,全局Configuration对象,会加载所有的mapper接口及XML信息,并封装到mappedStatements集合中。
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements;
我们又知道,MappedStatement对象封装了每个SQL语句的详细信息,并且它是一个final类型也就是说实例化之后就不允许改变。
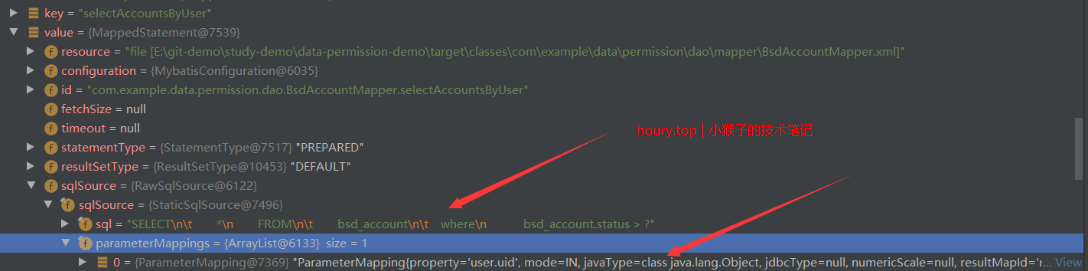
从上图可以看出,每个MappedStatement实例装载了很多信息,其中就封装了一个SqlSource接口的实例,SqlSource中封装了原始SQL和参数映射的关系。
StaticSqlSource源码:
public class StaticSqlSource implements SqlSource {
private final String sql;
private final List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings;
// Configuration对象
private final Configuration configuration;
// 构造方法
public StaticSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql) {
this(configuration, sql, null);
}
// 构造方法
public StaticSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings) {
this.sql = sql;
this.parameterMappings = parameterMappings;
this.configuration = configuration;
}
// 获取BoundSql对象
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
return new BoundSql(configuration, sql, parameterMappings, parameterObject);
}
}
3.2 ParameterMapping
加载SqlSource时,我们可以看到还加载了ParameterMapping对象,在SqlSource使用集合来封装每个参数的映射关系。
~~~java
private final List
采用#{var}的形式来引用变量时,其中的变量会在解析Mapper.xml文件中的语句时就被替换为占位符“?”,同时通过ParameterMapping类记录对应的变量信息。在真正执行对应的语句时会用传递的真实参数根据ParameterMapping信息给PreparedStatement设置参数,具体可参考PreparedStatementHandler的parameterize()方法实现。
由上可知,我们每个#{var}符号,都会产生一个ParameterMapping,我们先看下ParameterMapping源码:
private Configuration configuration;
// #{}中的属性 user.uid
private String property;
// 参数模式 IN
private ParameterMode mode;
// 参数类型 java.lang.Object
private Class<?> javaType = Object.class;
// JdbcType 数据库数据类型
private JdbcType jdbcType;
private Integer numericScale;
// 类型处理器
private TypeHandler<?> typeHandler;
// resultMap的ID
private String resultMapId;
// JDBC类型名称
private String jdbcTypeName;
// 表达式
private String expression;
}
3.3 初始化加载SqlSource
通过前面,我们可知,SqlSource加载了SQL语句及参数映射关系,执行SQL的时候,根据传入的参数,拼装参数到SQL中,进行数据库操作。那么SqlSource具体是怎么创建,parameterMappings又是怎么构建的呢。接下来跟踪源码分析下。SqlSource对象的构建,是在XMLStatementBuilder类中的parseStatementNode执行的。
~~~java SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(this.configuration, this.context, parameterTypeClass); ~~~
首先createSqlSource方法调用的是XMLLanguageDriver(XML语言驱动)进行解析。执行的是XMLScriptBuilder(XML脚本生成器)的parseScriptNode解析XML节点,创建SqlSource对象。
/**
* 解析XML及节点
* @return SqlSource
*/
public SqlSource parseScriptNode() {
// 1. 解析动态标签, 如果有${}占位符,就会标记为isDynamic=true
MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(context);
SqlSource sqlSource = null;
if (isDynamic) {
// 2. 有${} 创建 DynamicSqlSource
sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode);
} else {
// 3. 否则创建RawSqlSource
sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);
}
return sqlSource;
}
因为没有${}标签,所以进入 new RawSqlSource创建SqlSource实例对象,RawSqlSource是静态SqlSource。它比{@link DynamicSqlSource} 快,因为映射是在启动时计算的。RawSqlSource的构造方法会调用SqlSourceBuilder的parse进行SqlSource实例对象的创建。
/**
* SqlSource构造方法
* @param configuration Configuration
* @param sql XML中的SQL 带占位符
* @param parameterType 参数类型
*/
public RawSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, Class<?> parameterType) {
// 1. 创建 SqlSource 解析器,解析器会添加Configuration、别名注册器、类型处理器
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
// 2. 检查参数类型,如果没有指定,则设置为Object类型
Class<?> clazz = parameterType == null ? Object.class : parameterType;
// 3. SqlSource 解析器创建sqlSource
sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(sql, clazz, new HashMap<String, Object>());
}
然后调用SqlSourceBuilder.parse方法进行处理。
/**
* SqlSourceBuilder创建 SqlSource对象
* @param originalSql SELECT
* *
* FROM
* bsd_account
* where
* bsd_account.status > #{user.uid}
* @param parameterType class java.lang.Object
* @param additionalParameters size = 0 附加参数
* @return
*/
public SqlSource parse(String originalSql, Class<?> parameterType, Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) {
// 1. 创建参数隐射处理器、传入configuration、参数类型、附加参数。
ParameterMappingTokenHandler handler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler(configuration, parameterType, additionalParameters);
// 2. 创建#{} 占位符的通用解析器
GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", handler);
// 3. 通用解析器解析原始SQL,一顿操作,将#{} ,替换为? ,
String sql = parser.parse(originalSql);
// 4. 最终穿件静态的SqlSource返回
return new StaticSqlSource(configuration, sql, handler.getParameterMappings());
}
对#{}处理就是GenericTokenParser.parse方法了,他会替换占位符为?,获取占位符中的属性,创建参数映射关系。
/** 解析占位符
* SELECT
* *
* FROM
* bsd_account
* where
* bsd_account.status > #{user.uid}
* @param text
* @return
*/
public String parse(String text) {
// 1. 查看是否# { 开头
if (text == null || text.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
// search open token
int start = text.indexOf(openToken, 0);
if (start == -1) {
return text;
}
// 2. 原始SQL字符串转为char数组
char[] src = text.toCharArray();
int offset = 0;
final StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder expression = null;
while (start > -1) {
if (start > 0 && src[start - 1] == '\\') {
// this open token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset - 1).append(openToken);
offset = start + openToken.length();
} else {
// found open token. let's search close token.
if (expression == null) {
expression = new StringBuilder();
} else {
expression.setLength(0);
}
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset);
offset = start + openToken.length();
int end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
// 3. 获取#{}中配置的属性 赋值给expression
while (end > -1) {
if (end > offset && src[end - 1] == '\\') {
// this close token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset - 1).append(closeToken);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
} else {
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
break;
}
}
if (end == -1) {
// close token was not found.
builder.append(src, start, src.length - start);
offset = src.length;
} else {
// SELECT
// *
// FROM
// bsd_account
// where
// bsd_account.status >
//
// 4. handleToken 会添加?,处理参数映射
builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString()));
offset = end + closeToken.length();
}
}
start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset);
}
if (offset < src.length) {
builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset);
}
// 5. 返回处理后的SQL
return builder.toString();
}
在上述parse方法中,最重要的就是handleToken方法,他用来处理#{}占位符。这里调用的是SqlSourceBuilder.handleToken。
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
// 添加到 List<ParameterMapping>
parameterMappings.add(buildParameterMapping(content));
return "?";
}
构建参数映射关系,调用的是buildParameterMapping方法。
/**
* 创建 ParameterMapping
* @param content user.uid => #{}
* @return
*/
private ParameterMapping buildParameterMapping(String content) {
// 1. 创建Map property -> user.uid 处理参数
Map<String, String> propertiesMap = parseParameterMapping(content);
String property = propertiesMap.get("property"); // user.uid
Class<?> propertyType;
// 2. 获取参数的类型 class java.lang.Object
if (metaParameters.hasGetter(property)) { // issue #448 get type from additional params
propertyType = metaParameters.getGetterType(property);
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterType)) {
propertyType = parameterType;
} else if (JdbcType.CURSOR.name().equals(propertiesMap.get("jdbcType"))) {
propertyType = java.sql.ResultSet.class;
} else if (property == null || Map.class.isAssignableFrom(parameterType)) {
propertyType = Object.class;
} else {
MetaClass metaClass = MetaClass.forClass(parameterType, configuration.getReflectorFactory());
if (metaClass.hasGetter(property)) {
propertyType = metaClass.getGetterType(property);
} else {
propertyType = Object.class;
}
}
// 3. Builder构建ParameterMapping
ParameterMapping.Builder builder = new ParameterMapping.Builder(configuration, property, propertyType);
Class<?> javaType = propertyType;
String typeHandlerAlias = null;
// 4. 循环 property -> user.uid
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : propertiesMap.entrySet()) {
String name = entry.getKey(); // property
String value = entry.getValue(); // user.uid
// 5. 构建属性
if ("javaType".equals(name)) {
javaType = resolveClass(value);
builder.javaType(javaType);
} else if ("jdbcType".equals(name)) {
builder.jdbcType(resolveJdbcType(value));
} else if ("mode".equals(name)) {
builder.mode(resolveParameterMode(value));
} else if ("numericScale".equals(name)) {
builder.numericScale(Integer.valueOf(value));
} else if ("resultMap".equals(name)) {
builder.resultMapId(value);
} else if ("typeHandler".equals(name)) {
typeHandlerAlias = value;
} else if ("jdbcTypeName".equals(name)) {
builder.jdbcTypeName(value);
} else if ("property".equals(name)) {
// Do Nothing
} else if ("expression".equals(name)) {
throw new BuilderException("Expression based parameters are not supported yet");
} else {
throw new BuilderException("An invalid property '" + name + "' was found in mapping #{" + content + "}. Valid properties are " + parameterProperties);
}
}
if (typeHandlerAlias != null) {
builder.typeHandler(resolveTypeHandler(javaType, typeHandlerAlias));
}
// 6. 返回 ParameterMapping{property='user.uid', mode=IN, javaType=class java.lang.Object, jdbcType=null, numericScale=null, resultMapId='null', jdbcTypeName='null', expression='null'}
return builder.build();
}
最终根据处理都的SQL,参数映射关系,new了一个StaticSqlSource,最终的SqlSource就构建完成了。
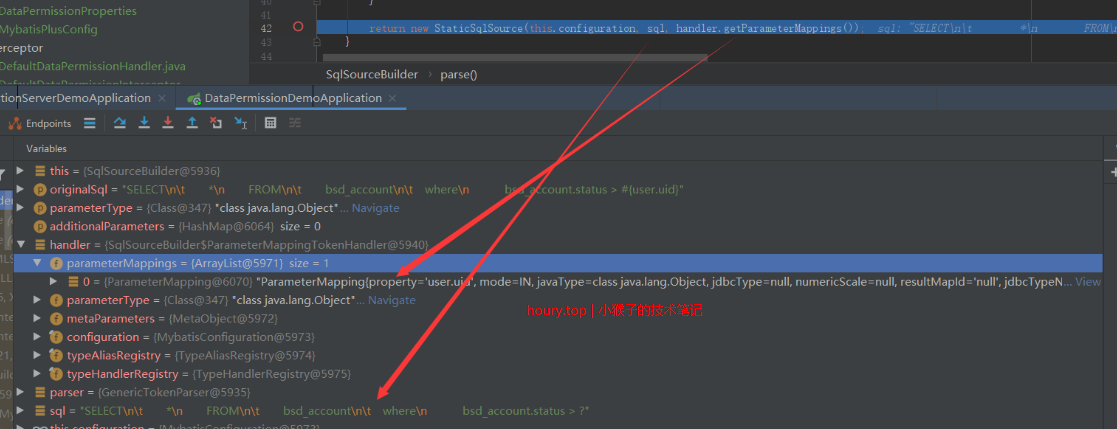
SqlSource最后被添加到了对应的MappedStatement中,在进行SQL操作时,会直接获取到mapper方法的SqlSource进行语句参数处理
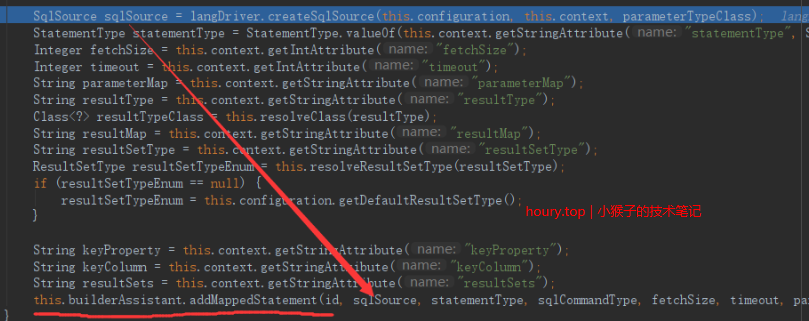
3.4 创建boundSql
执行SQL方法时,获取sqlSession,创建执行器,创建ParameterHandler,创建StatementHandler时,构造方法进入BaseStatementHandler,参数处理器、boundSql都是在构造方法中创建的。

之前说过SqlSource提供了getBoundSql方法,所以boundSql的创建是由SqlSource实例对象创建的。直接调用BoundSql的构造方法,传入带?好的SQL、参数隐射关系、用户输入的参数。

可以看到BoundSql对象中封装了SQL语句执行所需要的相关信息。

3.5 创建参数处理器
BaseStatementHandler构造创建了boundSql之后,就开始执行创建参数处理器了。
下一步进入Configuration对象的newParameterHandler方法,首先会调用DefaultParameterHandler的构造方法,将相关配置,SQL信息设置到对象中,返回ParameterHandler。
public DefaultParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
this.mappedStatement = mappedStatement;
this.configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration();
this.typeHandlerRegistry = mappedStatement.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry();
this.parameterObject = parameterObject;
this.boundSql = boundSql;
}

返回后,也使用了拦截器对其进行包装处理。
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler)this.interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
3.6 参数处理
在执行器进行创建Statement时,会调用StatementHandler 处理器的parameterize方法对参数进行处理。
// 准备语句
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// 调用StatementHandler.prepare
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// 调用StatementHandler.parameterize
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
参数处理最终调用的是DefaultParameterHandler中的setParameters方法。
//设置参数
@Override
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId());
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings != null) {
//设置参数
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
//循环设参数
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
//如果不是OUT,才设进去
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
//若有额外的参数, 设为额外的参数
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
//若参数为null,直接设null
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
//若参数有相应的TypeHandler,直接设object
value = parameterObject;
} else {
//除此以外,MetaObject.getValue反射取得值设进去
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();
if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {
//不同类型的set方法不同,所以委派给子类的setParameter方法
jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();
}
try {
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
} catch (TypeException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
3.7 返回
处理完成后,在Statement执行对象中,就生成了对应的完成SQL语句了,接下来继续执行查询,就完成了CRUD操作。