Mybatis-plus中的性能规范插件讲解
1. 前言
IllegalSQLInnerInterceptor :不规范SQL拦截器。由于开发人员水平参差不齐,即使订了开发规范很多人也不遵守,SQL是影响系统性能最重要的因素,所以拦截掉不规范SQL语句。
拦截SQL类型的场景 :
1.必须使用到索引,包含left join连接字段,符合索引最左原则
- 如果因为动态SQL,bug导致update的where条件没有带上,全表更新上万条数据
- 如果检查到使用了索引,SQL性能基本不会太差
2.SQL尽量单表执行,有查询left join的语句,必须在注释里面允许该SQL运行,否则会被拦截,有left join的语句,如果不能拆成单表执行的SQL,请leader商量在做,SQL尽量单表执行的好处:
- 查询条件简单、易于开理解和维护
- 扩展性极强;(可为分库分表做准备)
- 缓存利用率高
3.where条件为空
4.where条件使用了 !=
5.where条件使用了 not 关键字
6.where条件使用了 or 关键字
7.where条件使用了 使用子查询
2. 测试案例
配置类添加插件
// 添加sql性能规范插件
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new IllegalSQLInnerInterceptor());
return interceptor;
Mapper添加SQL
<select id="list" resultType="org.seata.service.order.entity.OrderTbl">
select * from order_tbl
</select>
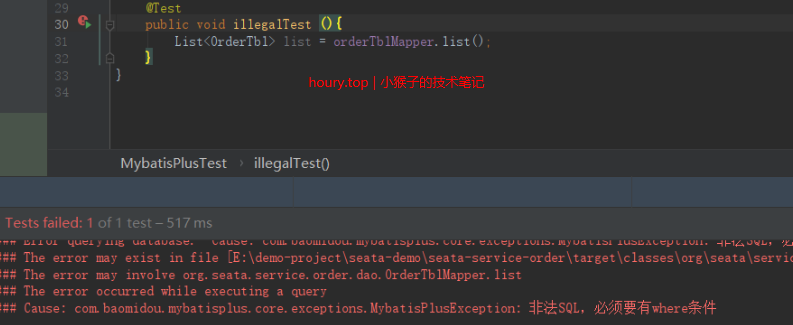
测试执行,发现此SQL没有添加条件,被拦截
可使用注解 @InterceptorIgnore(illegalSql = “1”)忽略此插件
@InterceptorIgnore(illegalSql = "1")
List<OrderTbl> list();
3. 源码分析
beforePrepare:前置处理。
public void beforePrepare(StatementHandler sh, Connection connection, Integer transactionTimeout) {
PluginUtils.MPStatementHandler mpStatementHandler = PluginUtils.mpStatementHandler(sh);
MappedStatement ms = mpStatementHandler.mappedStatement();
SqlCommandType sct = ms.getSqlCommandType();
// INSERT语句、添加了拦截忽略注解、存在SQL 解析缓存时不执行校验
if (sct == SqlCommandType.INSERT || InterceptorIgnoreHelper.willIgnoreIllegalSql(ms.getId())
|| SqlParserHelper.getSqlParserInfo(ms)) return;
BoundSql boundSql = mpStatementHandler.boundSql();
String originalSql = boundSql.getSql();
logger.debug("检查SQL是否合规,SQL:" + originalSql);
String md5Base64 = EncryptUtils.md5Base64(originalSql);
// 查询缓存是否已校验过
if (cacheValidResult.contains(md5Base64)) {
logger.debug("该SQL已验证,无需再次验证,,SQL:" + originalSql);
return;
}
parserSingle(originalSql, connection);
// 缓存验证结果
cacheValidResult.add(md5Base64);
}
processSelect:where条件校验,根据SQL类型,进入不同的校验方法。
protected void processSelect(Select select, int index, String sql, Object obj) {
// 使用JsqlParser解析SQL为select对象
PlainSelect plainSelect = (PlainSelect) select.getSelectBody();
Expression where = plainSelect.getWhere();
// 断言是否有where条件
Assert.notNull(where, "非法SQL,必须要有where条件");
Table table = (Table) plainSelect.getFromItem();
List<Join> joins = plainSelect.getJoins();
// 校验where
validWhere(where, table, (Connection) obj);
// 校验Join
validJoins(joins, table, (Connection) obj);
}
validWhere:验证where条件的字段,是否有not、or等等,并且where的第一个字段,必须使用索引
private void validWhere(Expression expression, Table table, Table joinTable, Connection connection) {
validExpression(expression);
if (expression instanceof BinaryExpression) {
//获得左边表达式
Expression leftExpression = ((BinaryExpression) expression).getLeftExpression();
validExpression(leftExpression);
//如果左边表达式为Column对象,则直接获得列名
if (leftExpression instanceof Column) {
Expression rightExpression = ((BinaryExpression) expression).getRightExpression();
if (joinTable != null && rightExpression instanceof Column) {
if (Objects.equals(((Column) rightExpression).getTable().getName(), table.getAlias().getName())) {
validUseIndex(table, ((Column) rightExpression).getColumnName(), connection);
validUseIndex(joinTable, ((Column) leftExpression).getColumnName(), connection);
} else {
validUseIndex(joinTable, ((Column) rightExpression).getColumnName(), connection);
validUseIndex(table, ((Column) leftExpression).getColumnName(), connection);
}
} else {
//获得列名
validUseIndex(table, ((Column) leftExpression).getColumnName(), connection);
}
}
//如果BinaryExpression,进行迭代
else if (leftExpression instanceof BinaryExpression) {
validWhere(leftExpression, table, joinTable, connection);
}
//获得右边表达式,并分解
Expression rightExpression = ((BinaryExpression) expression).getRightExpression();
validExpression(rightExpression);
}
}
validUseIndex:检查是否使用索引
private void validUseIndex(Table table, String columnName, Connection connection) {
//是否使用索引
boolean useIndexFlag = false;
String tableInfo = table.getName();
//表存在的索引
String dbName = null;
String tableName;
String[] tableArray = tableInfo.split("\\.");
if (tableArray.length == 1) {
tableName = tableArray[0];
} else {
dbName = tableArray[0];
tableName = tableArray[1];
}
List<IndexInfo> indexInfos = getIndexInfos(dbName, tableName, connection);
for (IndexInfo indexInfo : indexInfos) {
if (null != columnName && columnName.equalsIgnoreCase(indexInfo.getColumnName())) {
useIndexFlag = true;
break;
}
}
if (!useIndexFlag) {
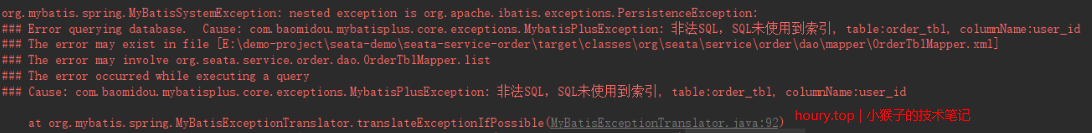
throw new MybatisPlusException("非法SQL,SQL未使用到索引, table:" + table + ", columnName:" + columnName);
}
}
validJoins:如果SQL用了 left Join,验证是否有or、not等等,并且验证是否使用了索引
private void validJoins(List<Join> joins, Table table, Connection connection) {
//允许执行join,验证jion是否使用索引等等
if (joins != null) {
for (Join join : joins) {
Table rightTable = (Table) join.getRightItem();
Expression expression = join.getOnExpression();
validWhere(expression, table, rightTable, connection);
}
}
}
验证通过后,会进入后续执行流程,否则会抛出异常
4. 总结
使用此插件,可以一定程度上规范SQL书写,也可以拓展自己的SQL规范逻辑。可以在开发环境中配置此插件,便于规范。